🛠 Technical Plan for Simulation Data Generation
This document provides a comprehensive technical description of the data generation mechanism in F²-Gen, an open-source platform for simulating scenario-based financial fraud datasets.
To learn about the underlying simulation engine, see the F²-Gen Engine. For hands-on use, refer to the Usage Guide.
1. Overview
The module is designed to generate test datasets for financial fraud detection, covering both normal and abnormal transactions.
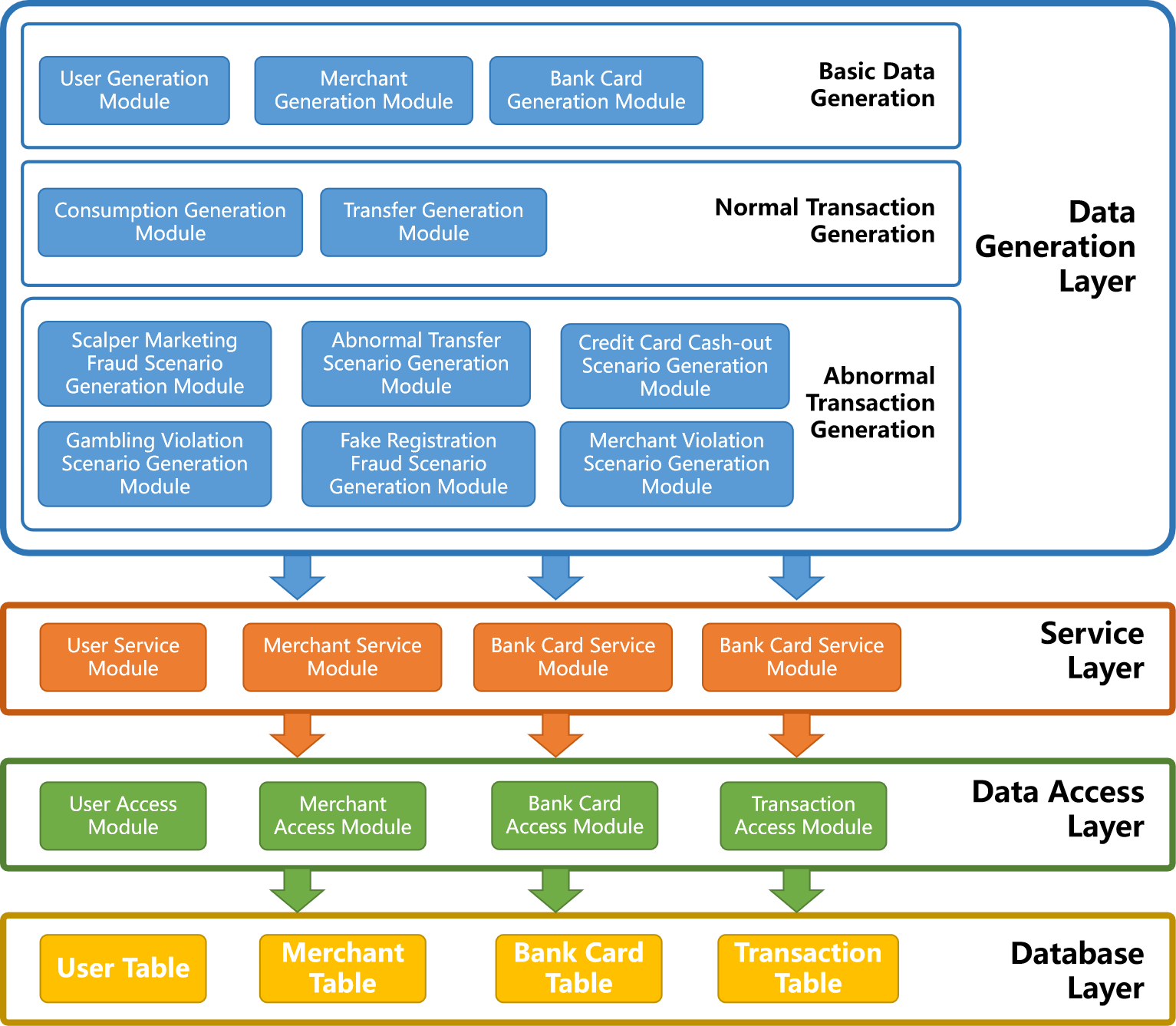
2. Technical Architecture
The system consists of four layers:
- Database Layer – Stores user, merchant, card, and transaction data.
- Data Access Layer – Interfaces with the database and serves the service layer.
- Service Layer – Provides services to the data generation modules.
- Data Generation Layer – Generates both normal and abnormal transactions.
3. Data Generation Pipeline
The generation process begins with creating base data (users, merchants, bank cards), followed by parallel generation of normal and abnormal transactions.
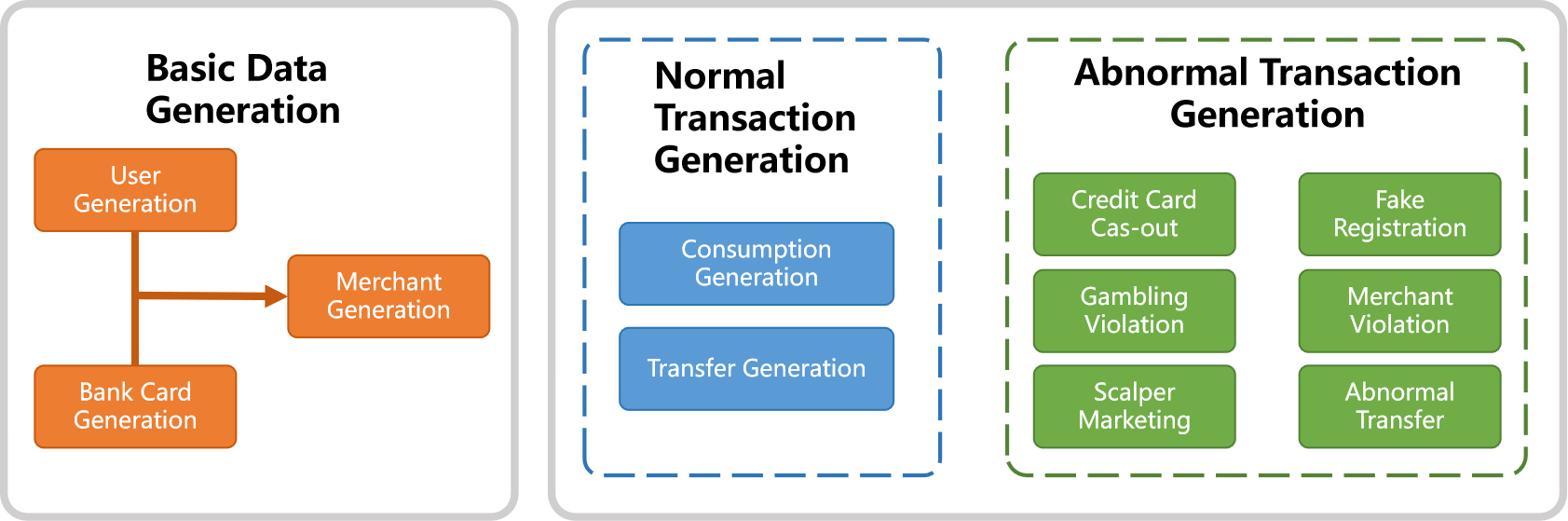
4. Base Data Generation
4.1 User Generation
Users are generated based on attributes like age, gender, occupation, and salary.
- Age: Sampled based on predefined distribution.
- Occupation: Sampled based on proportion and average salary.
- Salary: Derived from occupation salary range.
- Gender: Randomly assigned.
4.2 Merchant Generation
Merchants are generated using industry type, business hours, and spending range.
- Industry category and subcategory: Sampled from probability distribution.
- Business hours: Sampled probabilistically.
- Terminal ID and merchant ID: Randomly assigned.
- Spending range: Sampled according to industry norms.
4.3 Bank Card Generation
Card properties include card number, type, brand, and product.
- Card count: Mapped from salary level.
- Brand and product: Based on occupation and card distribution.
- Card grade: Derived from salary bracket.
5. Normal Transaction Generation
5.1 Consumption Simulation
- Users are assigned daily transaction frequency, consumption type, and levels.
- Transaction time and amount are sampled from configurations.
5.2 Transfer Simulation
- A user relationship graph is built (e.g., family).
- Transfers are generated between 1-hop and 2-hop neighbors.
6. Abnormal Scenario Simulation
6.1 Credit Card Cash-out
A three-stage fraud: identify suspects → simulate cash-out behavior → fund return via merchant transfer.
6.2 Gambling Violation
Users act as gamblers or money mules, simulating illegal transactions through platforms.
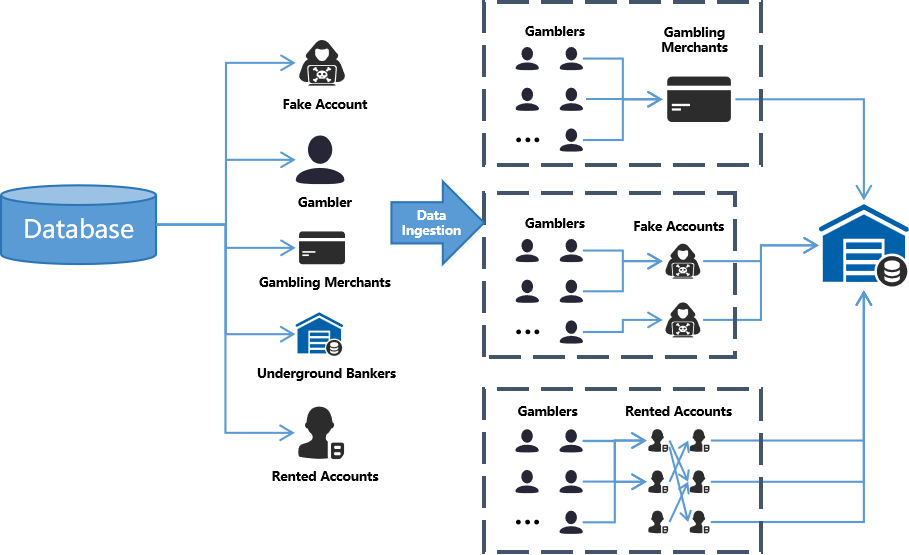
- Gambling user → gambling platform → underground bank
- Fake users act as transfer relays
- Rented accounts split incoming funds to conceal origins
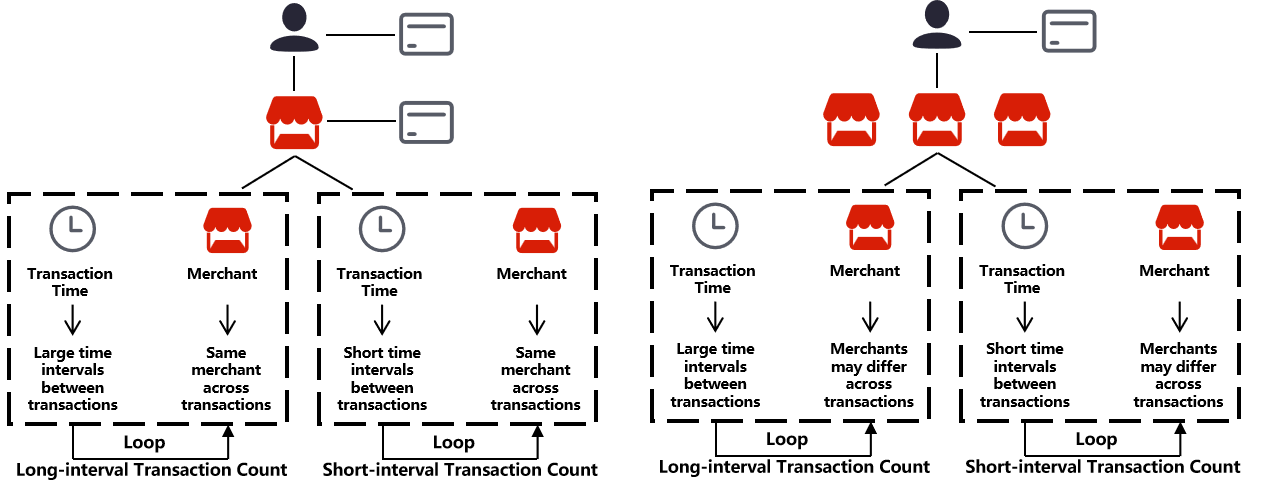
6.3 Scalper Marketing Fraud
Airdrop exploitation by scalpers simulating multiple low-value voucher purchases.
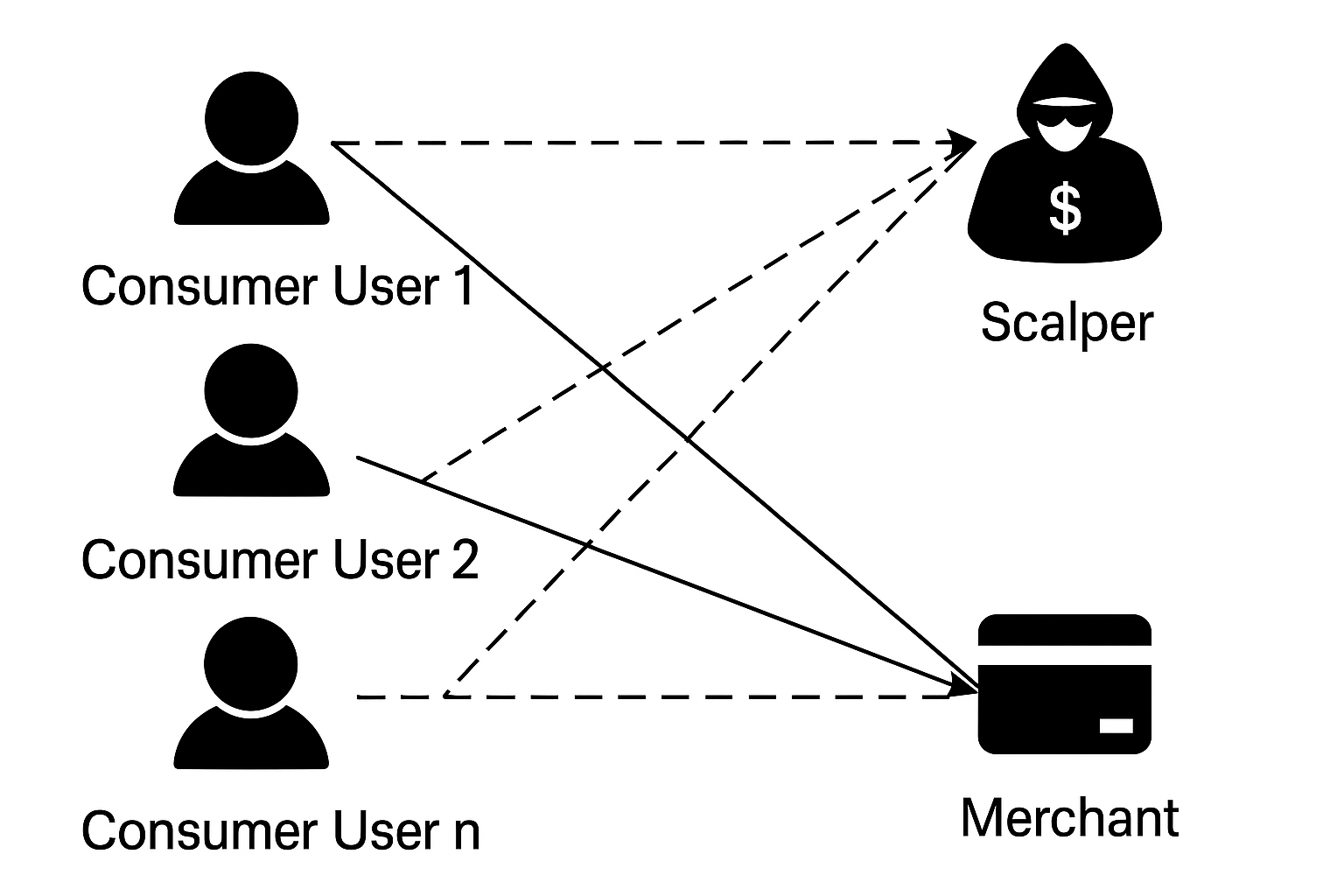
- Fraudulent users receive micro-transfers from normal users
- Small amount, high frequency, often during marketing campaign windows
6.4 Fake Registration Fraud
Simulates account takeover and unauthorized registrations using victim identity.
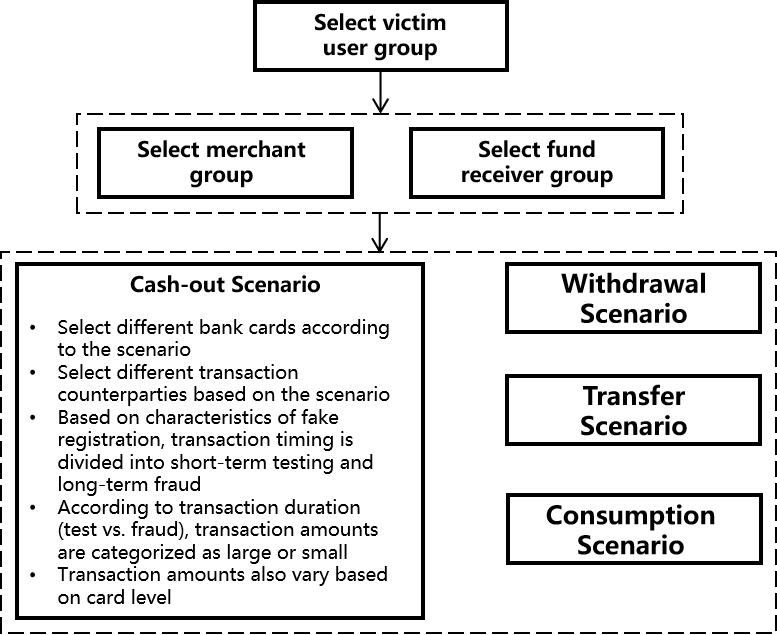
Includes:
- ATM withdrawal using fake identity
- Simulated POS transactions
- Illegal transfers and spending with cloned accounts
6.5 Merchant Violation Simulation
Models fraudulent merchant behavior such as terminal tampering or irregular billing.
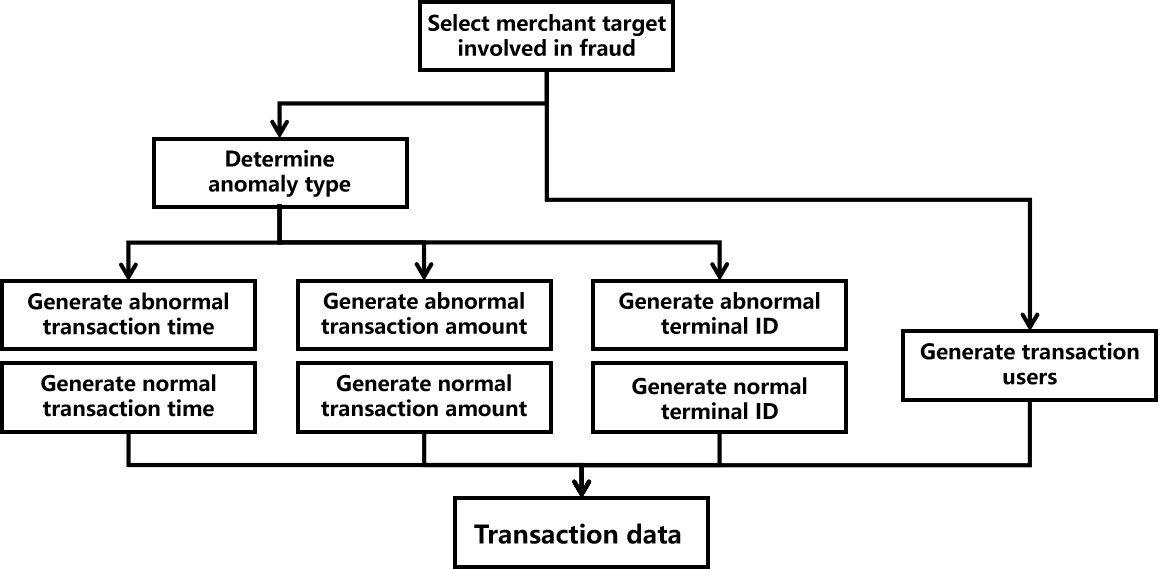
- Merchants labeled with different fraud types
- Custom logic per fraud type controls amount, timing, and terminal behavior
6.6 Abnormal Transfer (Telecom Fraud)
Victims wire money to scam groups, followed by laundering and distribution.

- Victim transfers → fraud ring’s receiving accounts
- Fund is split and distributed among ring members over time
✅ Notes
- All fraud simulation is parameterized and supports batch data export.
- Images used in this guide are hosted under
docs/assets/and referenced directly via relative paths.
📄 This technical plan is part of the official documentation of F²-Gen. For more modules and case studies, please refer to Usage Guide or return to the Homepage.